Cell Structure and Function:
All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells are the building blocks
of every organism’s body. These are the lowest levels of organ systems
that collectively make up an organism.
Cells contain several organelles which perform specific functions for
cells. Several other biomolecules like lipids, nucleic acids and proteins
are also found in cells. The hereditary material of cells is also present
inside the cells.
What is a Cell?
The
cell is the fundamental functional unit of life which cannot be seen with
the naked eye. Billions of cells are found in multicellular organisms
which are of different sizes, and shapes and perform different functions.
History of Cells:
The cell was first time described by
Robert Hooke
in 1665 while he was studying bottle cork of the tree bark using his own
compound microscope. He notices some small room-like structures in the
cork and named them cells. He called the cells non-living components
because he could not notice any movements in the cells due to the small
magnification power of his microscope.
Cell Theory;
Cell theory was developed by the two microbiologists
Schleiden
and
Schwann
which described the following properties of cells;
- All living things are made up of cells
- New cells are developed from the division of old cells
- Cells are the basic units or building blocks of life
Modern Concept About Cells:
In 1883,
Robert Brown, a Scottish botanist first described the nucleus of cells and gave the
first insight into the cells.
- The activity of an organism is dependent on the activity of
independent cells
- Energy flow in cells occurs by respiration through the breakage of
carbon dioxide
- cells
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms are different from each
other because prokaryotic organisms are unicellular and eukaryotic
organisms are multicellular. On the other hand, animal cells are different
from plant cells because animal cells do not have cell walls while plant
cells do. However, some common structures found in all cells are the
following;
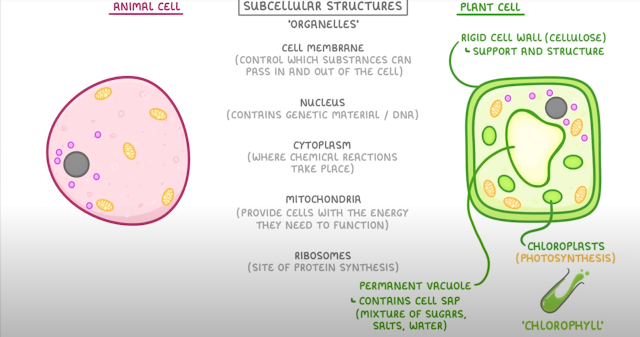
Cell Membrane
The Cell Envelop; Also known as plasma membrane, it is a selective permeable membrane that allows only selective
substances to pass through it. The cell membrane provides coverage by
enclosing the organelles. The cell membrane is formed of proteins, lipids and carbohydrates. It is a
semi-permeable membrane that allows the exchange of water, carbon dioxide
and oxygen. It also removes toxic substances from the cells.
Nucleus- The Brain of the Cell: The nucleus is the largest cell organelle which is present in the
center of the cell. The fluid present inside the nucleus is called
nucleoplasma. Each nucleus has a small body inside it which is
called nucleolus which prepare ribosomal RNA which are transported out
of the cell through nuclear pores. The nucleus is found in all cells of
the body except in red blood cells.
The nucleus contains DNA which is the genetic material of organisms and is
transferred from one generation to another at the time of division.
The nucleus controls all the metabolic activities of cells, stores genetic
information, manufactures protein components and helps in cell division
and synthesis of RNAs.
Cytoplasm: Cytoplasm is a thick jelly-like fluid present between the cell
membrane and the nucleus of cells. Organelles float in the cytoplasm.
All cellular activities and functions such as protein formation,
respiration, energy production, mitosis and meiosis, etc. take place in
the cytoplasm.
Mitochondria Powerhouses of Cells: Mitochondria are also known as the powerhouses of cells because they
generate energy for all metabolic activities of the cells. Mitochondria
contain their DNA.
Endoplasmic Reticulum-The Proteins Storage Factory: The endoplasmic reticulum is bound to the nuclear membrane. These are
of two types i.e. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum and Smooth Endoplasmic
Reticulum.
The rough endoplasmic reticulum is called so because it contains ribosomes
on its surface. It produces vesicles for protein packaging. Smooth
endoplasmic reticulum produces small amounts of lipids, proteins, and
carbohydrates. It also breaks down toxic substances in the cells.
Golgi Apparatus- The Protein Packaging Factory: Golgi apparatus or Golgi bodies
receive proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, modify their
structures, give them specific shapes and transfer them to specific
locations where these proteins are needed.
Ribosomes-The Protein Synthesis Factory: Ribosomes are floating organelles in the cells and are also found on
the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes make essential proteins for
various cellular functions therefore called protein manufacturing
factories of the cells.
Lysosomes-The Suicidal Bags of the Cells:
Lysosomes are small organelles in the cytoplasm of the cells that
contain hydrolytic enzymes. They digest the cells after the cells’ death
and destroy foreign particles such as pathogens.
The Storehouse of the Cells: vacuoles store different substances such as water, minerals, salts
and food materials. These are also called the storehouses of cells.
Cell performs the following functions such as;
- Cell provides support and structure for the whole body.
- It promotes growth by mitosis and meiosis.
- It provides energy for various metabolic functions.
- It helps in reproduction by cell division methods.
- It performs transportation functions such as transferring oxygen, nutrients and other essential substances by diffusion.
- It helps in metabolism by converting food into energy.







0 Comments